Octacarbonyl dicobalt
-
Product Name :
Octacarbonyl dicobalt
-
CAS No :
10210-68-1
-
Project State :
Commercial
Application
General Description
Good factory exports good Octacarbonyl dicobalt 10210-68-1
- Molecular Formula:C8Co2 O8
- Molecular Weight:341.94
- Appearance/Colour:crystalline solid
- Vapor Pressure:9.333-200Pa at 15-25℃
- Melting Point:51-52 °C
- Boiling Point:52 deg C
- Flash Point:-13 °C
- PSA:0.00000
- Density:1.81
- LogP:-1.66400
COBALT CARBONYL(Cas 10210-68-1) Usage
|
Reaction |
Reagent for the Pauson-Khand conversion of an olefin, an alkyne and carbon monoxide into a cyclopentenone. Precatalyst in combination with triphenylphosphite for the cataytic Pauson-Khand reaction. Catalyzes the rearrangement of 1-alkynylcyclopropanols to cyclopentenones. Catalyzes the conversion of aziridines to β-lactams. Catalyzes the conversion of diallylanilines and aryliminies to quinolines. Reagent for the selective cleavage of benzyl ethers. Domino Nicholas and Pauson-Khand process induced by nitroarene reduction. |
|
Sources |
Adkins, Homer., and G. Krsek. JACS 71.9(1949):3051-3055. Feder, Harold M., and J. Halpern. Cheminform 7.7(1976):no-no. Seitz, Friedrich, and M. S. Wrighton. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 27.2(1988):289-291. Antebi, Shlomo, and H. Alper. Tetrahedron Letters 16.38(1985):no-no. Krafft, Marie E., L. V. R. Bo?aga, and C. Hirosawa. Cheminform 32.37(2001):no-no. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dicobalt_octacarbonyl |
|
Preparation |
Cobalt octacarbonyl is prepared by the reaction of finely divided cobalt with carbon monoxide under pressure: 2Co + 8CO → Co2(CO)8 The compound may be prepared in a similar way from cobalt(II) iodide. Also, it may be prepared by thermal decomposition of cobalt carbonyl hydride: 2HCo(CO)4 → Co2(CO)8 + H2 |
|
Hazard |
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. |
|
Health Hazard |
Dicobalt octacarbonyl exhibits moderate toxicityby inhalation route and somewhatlower toxicity by intraperitoneal and oralroutes. However, it is much less toxicthan nickel tetracarbonyl or iron pentacarbonyl.A 2-hour LC50 value in mice isreported as 27 mg/m3 (Lewis 1996). Anoral LD50 value in rats is within the rangeof 750–800 mg/kg. It decomposes, evolvingtoxic carbon monoxide. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by inhalation and intraperitoneal routes. Questionable carcinogen. Decomposes in air to form a product that ignites spontaneously in air. "hen heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and fumes. See also CARBONYLS and COBALT COMPOUNDS. |
|
Potential Exposure |
This material is used as a catalyst for a number of reactions. It is also used in antiknock gasoline and for high-purity cobalt salts. |
|
Shipping |
UN3124 Toxic solids, self-heating, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; 6.1-Poisonous materials, 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material. Technical Name Required. UN3190 Self-heating solid, inorganic, Hazard Class: 4.2; Labels: 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material, Technical Name Required. UN1325 Flammable solid, organic, n.o.s. Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid |
|
Purification Methods |
It forms orange-brown crystals on recrystallisation from n-hexane under a carbon monoxide atmosphere [Ojima et al. J Am Chem Soc 109 7714 1987; see also Hileman in Preparative Inorganic Reactions, Ed. Jolly, Vol 1 p 101 1987]. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Decomposes on exposure to air or heat (@ ~52°C) producing toxic fumes of cobalt and oxides of carbon |
|
General Description |
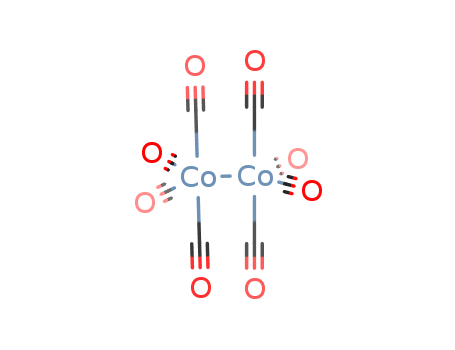
Cobalt carbonyl (Co2(CO)8), also known as dicobalt octacarbonyl or octacarbonyldicobalt, is an organometallic compound consisting of two cobalt atoms bridged by carbonyl ligands. It is a volatile, orange-colored solid or liquid at room temperature, widely used as a catalyst in organic synthesis, particularly in hydroformylation and carbonylation reactions. COBALT CARBONYL is highly toxic and flammable, requiring careful handling due to its sensitivity to air and moisture. Its structure features a Co-Co bond with terminal and bridging carbonyl groups, making it a key example of transition metal carbonyl chemistry. |
|
Physical properties |
Orange crystals; density 1.78 g/cm3; melts at 5l°C; decomposes above this temperature; insoluble in water; soluble in most organic solvents including alcohol, ether, carbon disulfide. |
InChI:InChI=1/8CO.2Co/c8*1-2;;/q8*-1;2*+2/rC8Co2O8/c11-1-9(2-12,3-13,4-14)10(5-15,6-16,7-17)8-18/q-4


